3 KafkaFlow Features Hard to Ignore
If you are a .NET developer working with Apache Kafka, KafkaFlow is a framework worth exploring.
Here, you can find three compelling features that make KafkaFlow stand out and deserve your attention.
1️⃣ Multi-Threaded Consumers
In the typical Apache Kafka infrastructure, you will find topics with multiple partitions. If you observe a lag and need to increase the consumption throughput, you will do it by bringing new consumers into the consumer group. That strategy will work up to a point. The number of partitions works as an upper limit, and having more consumers in a consumer group than the number of partitions is useless. However, traditional single-threaded consumers may result in underutilized infrastructure resources.
KafkaFlow addresses this by offering multi-threading within a single consumer. This feature allows your consumer to delegate work to multiple workers, enabling parallel processing.
If that didn't catch your attention, let me tell you that even with multiple workers, KafkaFlow maintains message order. And all of that is perfectly encapsulated under a simple configuration.
// KafkaFlow Configuration
services.AddKafka(kafka => kafka
.AddCluster(cluster => cluster
.WithBrokers(new[] { "localhost:9092" })
.AddConsumer(consumer => consumer
.Topic("topic-name")
.WithGroupId("group-name")
.WithBufferSize(100)
.WithWorkersCount(10) // Define the number of workers
...
)
)
);This feature offers another option to scale consumption and use the infrastructure efficiently.
2️⃣ Administration API and Dashboard
KafkaFlow offers an Administration API and a Dashboard, providing a convenient way to manage your Apache Kafka consumers.
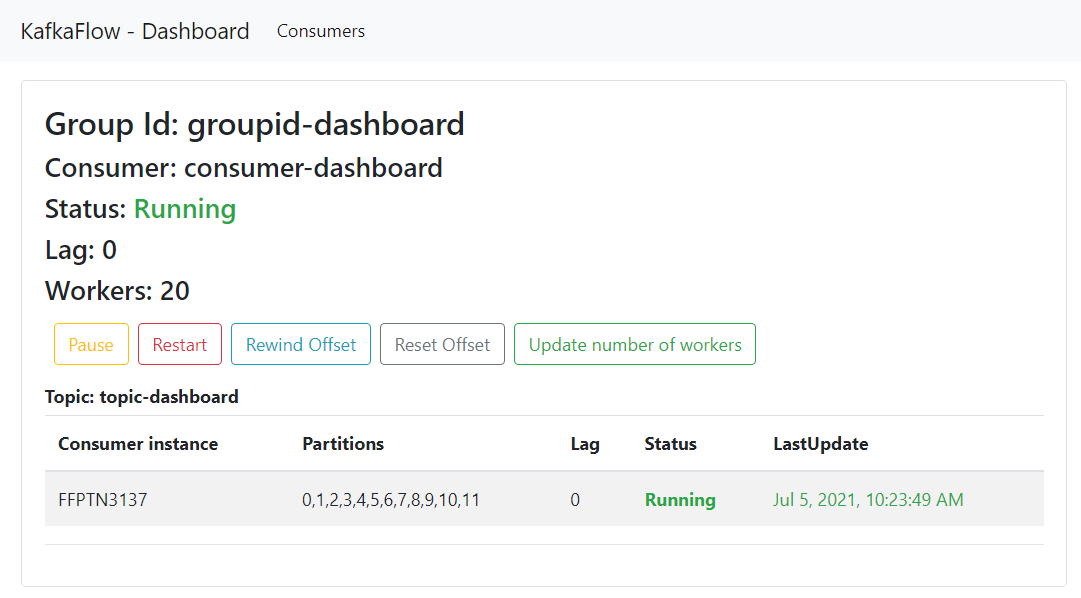
To set up the Dashboard, install the KafkaFlow Dashboard package, define the topic for administration messages, and call the UseKafkaFlowDashboard method in your web application.
builder.Services
.AddKafka(kafka => kafka
.AddCluster(cluster => cluster
.WithBrokers(new[] { "localhost:9092" })
.AddConsumer(consumer => consumer
...
)
.EnableAdminMessages("kafka-flow.admin") // Administration messages topic
.EnableTelemetry("kafka-flow.admin")
))
.AddControllers();
var app = builder.Build();
app.MapControllers();
app.UseKafkaFlowDashboard(); // Enable DashboardAccessing the Dashboard through a web application allows you to administrate consumers. The API exposes endpoints for various actions, such as pausing, starting, and stopping consumers, making it a valuable operational tool. All those actions are not only available through the Dashboard UI but also through a C# client.
3️⃣ Batch Consuming
While Kafka is excellent for handling real-time systems, processing one message at a time may not always be ideal. KafkaFlow introduces Batch Consuming, a useful feature in scenarios such as when you have devices producing numerous events and need to process them in bulk.
To enable Batch Consuming, install the corresponding package and add a middleware in your consumer configuration. Specify the batch size and batch timeout to control when the batch should be forwarded to the next middleware.
services.AddKafka(kafka => kafka
.AddCluster(cluster => cluster
.WithBrokers(new[] { "localhost:9092" })
.AddConsumer(
consumerBuilder => consumerBuilder
...
.AddMiddlewares(
middlewares => middlewares
...
.AddBatching(100, TimeSpan.FromSeconds(10)) // Configuration of the BatchConsumeMiddleware
.Add<HandlingMiddleware>() // Middleware to process the batch
)
)
)
);This feature allows KafkaFlow to collect messages until either the batch size or the defined time is reached, forwarding the batch to the next middleware. It is particularly handy for scenarios where you want to store events in a file or a database in a bulk change.
In conclusion, KafkaFlow brings valuable features for .NET developers working with Apache Kafka. Whether you need multi-threaded consumers, an Administration API with a Dashboard, or Batch-consuming capabilities, KafkaFlow provides a user-friendly and powerful solution. Consider adopting KafkaFlow as your .NET Kafka client to simplify your Kafka-based applications.